Introduction: Why Repressuring a Boiler Matters
Modern central heating systems rely on consistent water pressure to operate efficiently. When the pressure drops too low, your boiler may stop heating properly, radiators can become uneven, and you might even face system lockouts that leave your home cold. This is where a repressuring a boiler process becomes essential. By restoring the right balance of water pressure, you not only ensure steady heat throughout your home but also protect the system from long-term damage.
Low boiler pressure often occurs due to small leaks, recent radiator bleeding, or natural pressure loss over time. Fortunately, repressuring a boiler is usually straightforward, especially if your system includes a filling loop or digital control panel that guides the process. For most homeowners, it’s a safe DIY fix that takes only a few minutes with minimal tools.
Ignoring boiler pressure issues can have costly consequences. A system running under low pressure has to work harder, which increases wear and reduces efficiency. In severe cases, it may even lead to damaged pumps or heat exchangers. By learning how to repressurize correctly, you’ll save money on energy bills, avoid unnecessary repairs, and maintain a warm, comfortable home.
This guide will walk you through what you need before starting, a step-by-step process to safely repressurize your boiler, common mistakes to avoid, and expert tips to keep your heating system in top shape. With the right approach, repressuring a boiler becomes a simple routine task every homeowner can manage.

What You’ll Need Before You Start
Before attempting repressuring a boiler, it’s important to gather the right tools and ensure you’re working safely. Fortunately, most modern boilers are designed to make this process simple, and you won’t need many items. However, preparation will help you avoid mistakes and get the job done efficiently.
First, check your boiler’s user manual. It provides model-specific instructions for locating the filling loop or digital controls. If you don’t have a physical copy, most manuals are available online. Knowing where your pressure gauge, filling valves, and reset buttons are located is essential before you begin.
You’ll also need a clean, dry cloth to wipe away any condensation or dust from the gauge and valves. This ensures accurate readings and prevents dirt from entering the system. Some homeowners also keep a small container or towel nearby to catch any drips of water when operating the filling loop.
Protective gear is recommended, especially gloves. While repressuring is generally safe, it involves handling valves connected to the water system. Wearing gloves helps you maintain a firm grip and avoid minor injuries. Good lighting is equally important—make sure the area around your boiler is well-lit so you can see the controls clearly.
Finally, check your current boiler pressure. Most systems should read between 1.0 and 1.5 bar when cold. If your gauge shows less than 1.0 bar, you’ll need to add water to the system. By preparing with the right information and simple supplies, you’ll be ready to carry out repressuring a boiler quickly and safely.
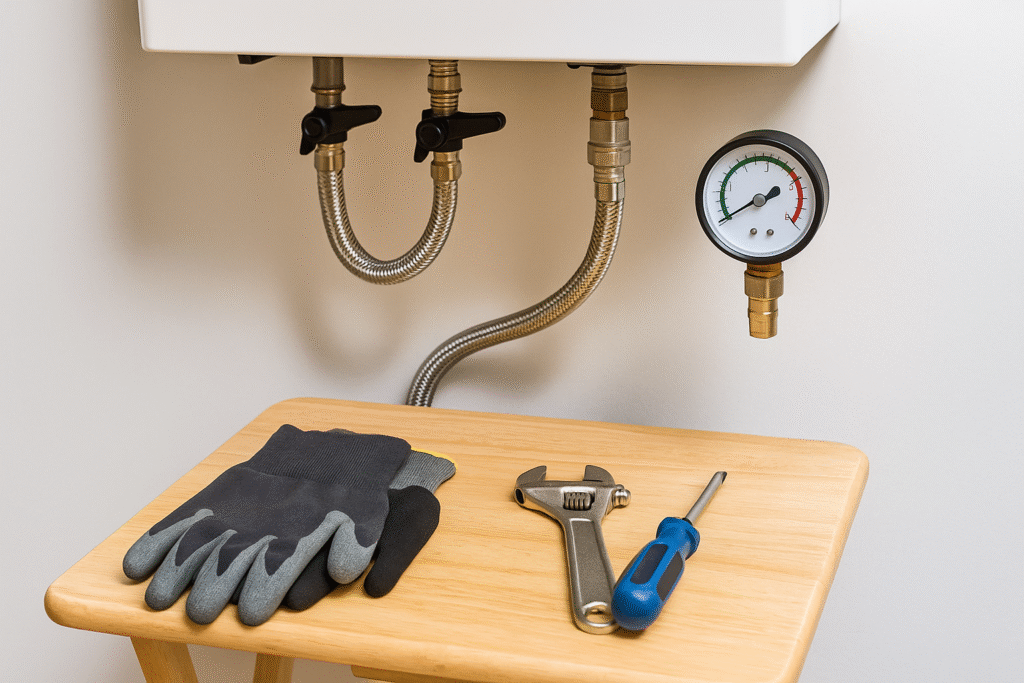
Step 1: Check the Current Pressure
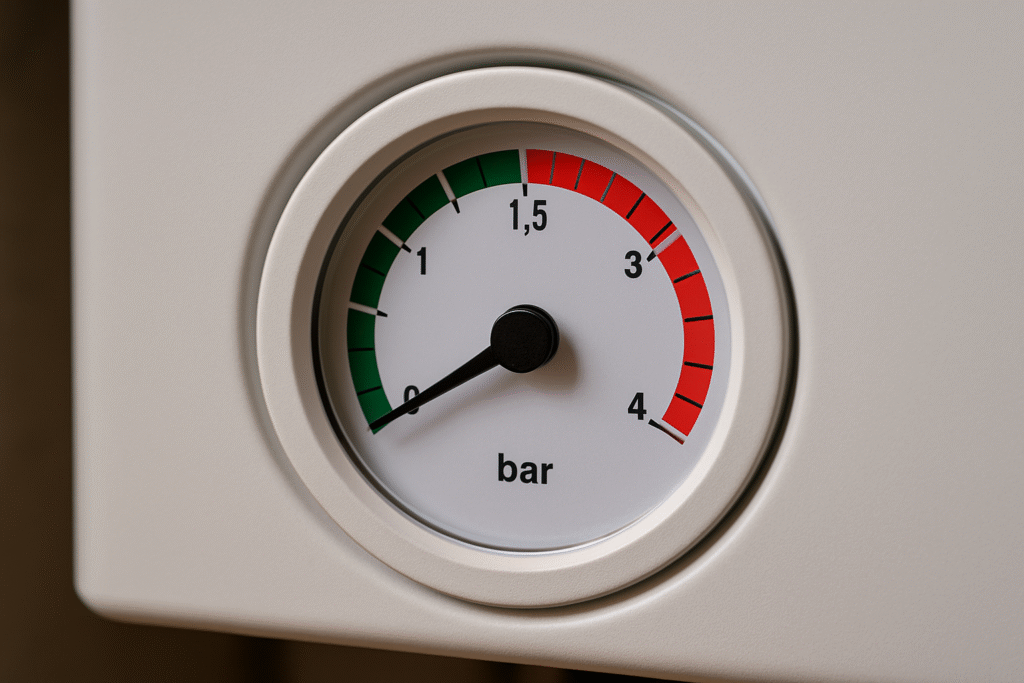
Before you begin repressuring a boiler, the first step is to check the system’s current pressure level. This will confirm whether the boiler actually needs repressuring and provide a baseline for the adjustments you’re about to make. Most boilers have a built-in pressure gauge located on the front panel or just beneath the unit. The gauge typically shows pressure in bars, with green, red, and sometimes yellow zones to indicate safe and unsafe levels.
When the system is cold, your pressure gauge should read between 1.0 and 1.5 bar. If it falls below 1.0, your heating system is likely under-pressured, which can cause issues such as uneven radiator heating, noisy operation, or the boiler locking out altogether. On the other hand, if the gauge is in the red zone above 2.5 or 3.0 bar, it means the system is over-pressured and may require bleeding or professional attention.
To check the reading, ensure your heating system is off and the boiler has cooled down. Pressure readings are most accurate when the system isn’t running. If you see a low reading, you’ll know that repressuring a boiler is necessary. If the pressure is normal but you’re still experiencing problems, the issue may be unrelated to pressure, and it’s worth consulting your user manual or calling a professional.
By identifying the current pressure level, you establish whether repressuring is required and can proceed with confidence to the next step in the process.

Step 2: Locate and Open the Filling Loop
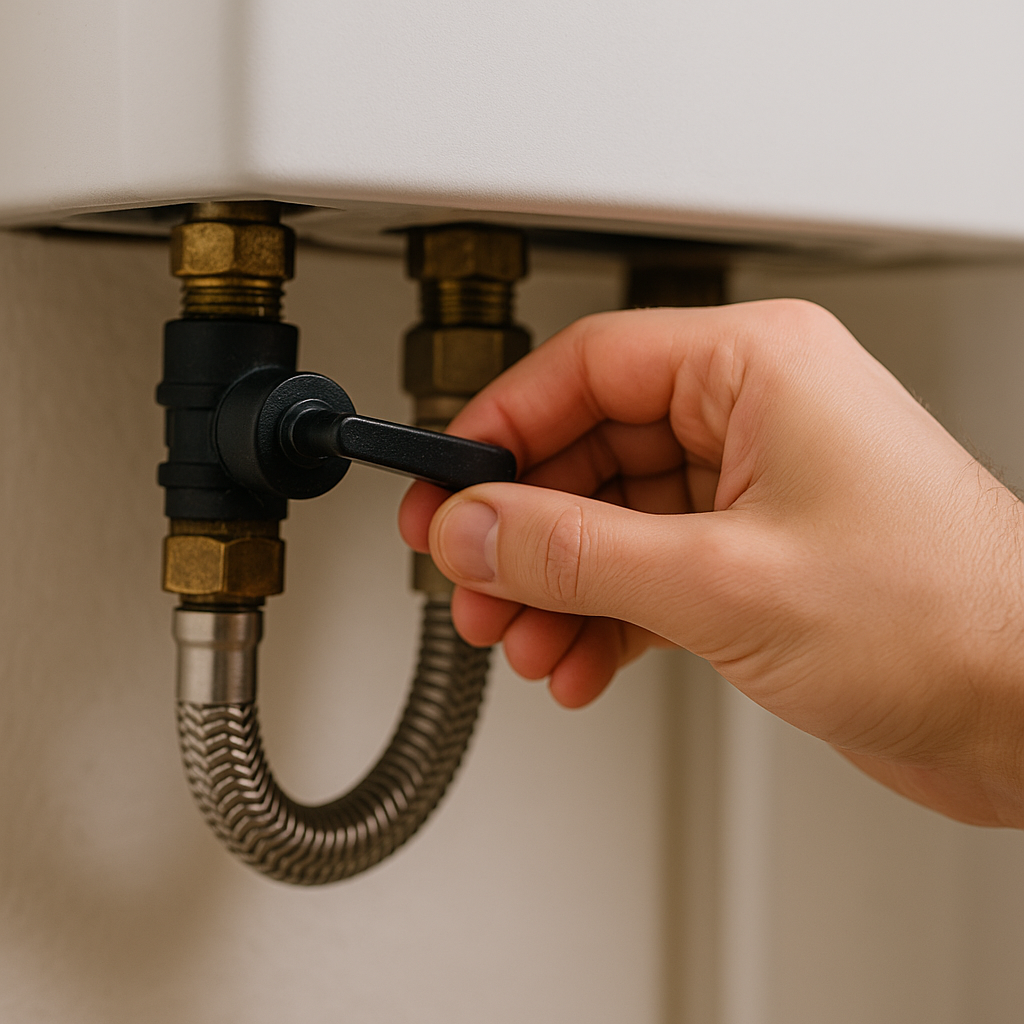
Once you’ve confirmed low pressure, the next stage in repressuring a boiler is to find the filling loop. This is the component that allows water to enter the heating system from your mains supply. In most modern combi boilers, the filling loop is a small, flexible silver hose with two black-handled valves, usually located directly beneath the boiler. Some systems may have an internal filling mechanism, which is often controlled via a switch or button on the display panel.
Before touching the filling loop, double-check your boiler’s manual. This will confirm its exact location and provide diagrams if needed. Once found, ensure both ends of the loop are securely connected. Loose fittings can cause leaks during the process. If your boiler has a keyed filling loop, insert the key into the slot before turning the valve.
To begin repressuring, turn both valves slowly to the open position. You should hear the sound of water entering the system. Watch the pressure gauge carefully as the needle starts to rise. The goal is to increase the reading to between 1.0 and 1.5 bar. Do not leave the valves unattended during this process, as over-pressurizing can cause long-term damage to your boiler.
Opening the filling loop correctly is the most hands-on part of repressuring a boiler. By following this step carefully, you ensure water enters the system safely and your pressure is restored without leaks or risks.

Step 3: Close the Valves and Check the Pressure Gauge
Once the pressure gauge shows a reading between 1.0 and 1.5 bar, it’s time to stop the water flow. Carefully close both valves on the filling loop by turning them back to their original position. You should hear the sound of water stop immediately. Double-check that both valves are fully shut—leaving them slightly open can cause the boiler to over-pressurize, which may trigger the safety release valve or cause leaks.
Next, remove the filling loop if your boiler has a detachable one. Some models require that the flexible hose be disconnected after use to comply with safety standards. Place a small container or towel beneath the valves before unscrewing the ends to catch any drips of water. If your boiler uses an integrated filling system, no disconnection is necessary.
Once the valves are closed, monitor the pressure gauge again. If the reading has stabilized within the safe range, your system is now properly repressurized. If the pressure continues to drop after a few minutes, this may indicate a leak elsewhere in the system, in which case you’ll need to investigate further or call a professional.
Finally, reset your boiler if required and turn the heating back on. Radiators should now heat evenly, and your boiler should run smoothly without warning lights or errors. By completing this step, you’ve successfully finished repressuring a boiler and ensured your system is operating safely.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Repressuring a Boiler
Even though repressuring a boiler is a relatively simple task, homeowners often make avoidable mistakes that can create bigger problems. Knowing these pitfalls in advance helps you stay safe and avoid costly repairs.
One of the most common mistakes is over-pressurizing the system. Turning the filling loop valves too far or leaving them open for too long can push the pressure beyond the safe range (usually above 2.5 bar). This may trigger the pressure relief valve or cause leaks in the system. Always monitor the gauge closely and stop filling once the needle is in the 1.0 to 1.5 bar range.
Another mistake is forgetting to close the valves fully after repressuring. Even a partially open valve will allow more water to enter the system, gradually increasing pressure until a fault occurs. Always return valves to their closed position and confirm that the water flow has stopped.
Homeowners sometimes attempt repressuring without checking for leaks. If there’s an underlying issue such as a leaking radiator, repressuring alone won’t solve the problem. In fact, it will cause the pressure to drop again quickly, requiring repeated top-ups. Identifying leaks first prevents unnecessary work and damage.
Finally, failing to consult the boiler manual or ignoring model-specific requirements can lead to errors. Some boilers have unique repressuring systems or require a reset after the process. Following the correct procedure ensures your boiler continues to function safely and efficiently.
Alternative Methods for Repressuring a Boiler
Not all boilers use the same type of filling loop, and understanding the alternatives can help if your system looks different. While most modern combi boilers rely on a flexible silver hose with valves, some models include a built-in filling key or electronic control system.
Keyed filling systems require inserting a special plastic key into a slot beneath the boiler. Once inserted, turning the key opens the valve and allows water into the system. The process is similar to using a filling loop but requires the key to start and finish the operation.
Other boilers may feature automatic repressuring systems. These electronically controlled systems detect low pressure and add water without manual intervention. While convenient, they still require occasional monitoring to ensure the system isn’t masking leaks or faults.
If your boiler doesn’t have a traditional filling loop, consult your manual or manufacturer’s website for guidance. Attempting to repressurize without knowing the correct method can damage the system. In some cases, you may need professional assistance to avoid complications.
By understanding alternative repressuring methods, you ensure that no matter what type of boiler you own, you can safely and effectively restore the correct pressure.
Expert Tips and Best Practices
Experts recommend several best practices when repressuring a boiler. First, always turn the boiler off and allow it to cool before starting. This ensures accurate pressure readings and prevents hot water from circulating during the process.
Make repressuring a routine check. Monitoring your boiler pressure monthly helps you catch issues before they become serious. Sudden or frequent drops in pressure often signal leaks or faulty components, which require professional attention.
Avoid adding too much water at once. Open the valves slowly and in small increments to give the system time to equalize. Rushing can lead to overshooting the safe range and create stress on the boiler.
Experts also stress the importance of regular maintenance. Bleeding your radiators once or twice a year helps maintain balanced pressure, while scheduling annual boiler servicing ensures that safety valves, pumps, and seals remain in good condition.
For further guidance on heating system maintenance, see the U.S. Department of Energy heating maintenance guide, which provides detailed safety tips for homeowners.
Frequently Asked Questions About Repressuring a Boiler
How often should I repressurize my boiler?
Most boilers maintain steady pressure for months at a time. If you’re repressuring more than once every few weeks, it may signal a leak or faulty component that needs repair.
What happens if I over-pressurize?
Over-pressuring can trigger the pressure relief valve, causing water discharge and potential system stress. Always aim for 1.0–1.5 bar when the system is cold.
Can repressuring fix all boiler problems?
No. While it resolves low-pressure issues, it won’t repair leaks, faulty pumps, or worn seals. If your pressure drops repeatedly, contact a professional.
Is repressuring safe for all boilers?
Yes, if done according to the manufacturer’s instructions. However, if you’re unsure, always consult your manual or hire a certified engineer.
For more detailed information on boiler operation, visit the Wikipedia entry on boilers.
 Read Similar Topics
Read Similar Topics
- Fix Moen Shower Valve
- Door Latch Not Fully Retracting
- Ceiling Water Damage
- Dishwasher Replacement Cost
- Unsticking a Zipper
Conclusion: Putting It All Together
Learning how to perform repressuring a boiler is a valuable skill that saves time, money, and stress. By monitoring your pressure gauge, preparing the right tools, following step-by-step instructions, and avoiding common mistakes, you ensure your heating system runs efficiently year-round.
While the process is simple, it’s also important to remain cautious. Over-pressurizing, ignoring leaks, or skipping safety checks can create bigger problems. By applying expert tips and consulting your manual, you’ll know when to manage it yourself and when to call a professional.
With routine maintenance and occasional repressuring, your boiler will provide consistent warmth and comfort. Ultimately, this straightforward process empowers homeowners to maintain their heating systems confidently and effectively.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window) Facebook
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window) LinkedIn
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window) X
- Click to share on Threads (Opens in new window) Threads
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp





Pingback: Proven Methods: How To Fix A Tear In Leather Shoes
Pingback: Proven Steps To Fix Moen Shower Valve Issues Fast
Pingback: Bathtub Baking Soda: Amazing Ways To Clean